|
De sinus, cosinus en tangens
-
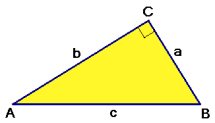
$sin(\angle A)=\frac{a}{c}$
-
$cos(\angle A)=\frac{b}{c}$
-
$tan(\angle A)=\frac{a}{b}$
|
Voorbeeld
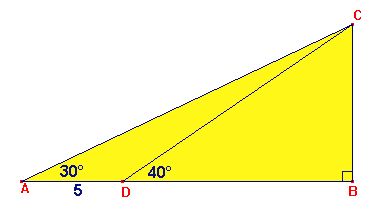
In $\Delta ABC$ geldt:
-
$\angle A=30^o$ en $\angle BDC=40^o$
-
$AD=5$
Bereken $BC$ op 1 decimaal nauwkeurig.
|
|
Tips en afspraken
Afspraak: benader (tenzij anders gevraagd) hoeken in één decimaal nauwkeurig.
Tip: Reken door met tusssenresultaten zonder af te ronden. Gebruik Ans of de geheugenplaatsen van de GR.
|
Vergelijkingen bij goniometrische berekeningen
$
\begin{array}{l}
x \cdot \tan (74^\circ ) = (x + 10)\tan (52^\circ ) \\
x \cdot \tan (74^\circ ) = x \cdot \tan (52^\circ ) + 10 \cdot \tan (52^\circ ) \\
x \cdot \tan (74^\circ ) - x \cdot \tan (52^\circ ) = 10 \cdot \tan (52^\circ ) \\
x(\tan (74^\circ ) - \tan (52^\circ )) = 10 \cdot \tan (52^\circ ) \\
x = \frac{{10 \cdot \tan (52^\circ )}}{{\tan (74^\circ ) - \tan (52^\circ )}} \approx 5,80 \\
\end{array}
$
|
|
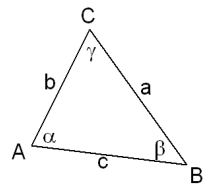
In een willekeurige driehoek ABC geldt:
|
Cosinusregel:
-
$a^{2}=b^{2}+c^{2}-2bccos(\alpha)$
-
$b^{2}=a^{2}+c^{2}-2accos(\beta)$
-
$c^{2}=a^{2}+b^{2}-2abcos(\gamma)$
Sinusregel:
-
$\Large\frac{a}{sin(\alpha)}$=$\Large\frac{b}{sin(\beta)}$=$\Large\frac{c}{sin(\gamma)}$
|
|
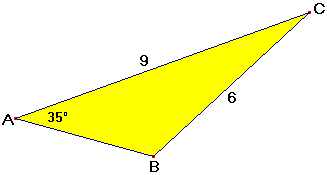
Voorbeeld 1
-
Bereken $\angle B$ in hele graden nauwkeurig.
|
Uitwerking
$
\begin{array}{l}
\frac{6}{{\sin 35^\circ }} = \frac{9}{{\sin \beta }} \\
6 \cdot \sin \beta = 9 \cdot \sin 35^\circ \\
\sin \beta = \frac{{9 \cdot \sin 35^\circ }}{6} \approx 0,860 \\
\beta \approx 59^\circ \,\,of\,\,\beta \approx 121^\circ \\
\end{array}
$
Die $59^o$ kan je goed zien als je $\Delta ABC$ gaat construeren.
|
|
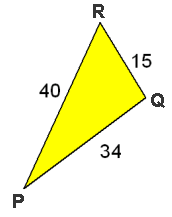
Voorbeeld 2
-
Bereken $\angle P$ in hele graden.
|
Uitwerking
$
\begin{array}{l}
15^2 = 40^2 + 34^2 - 2 \cdot 40 \cdot 34 \cdot \cos \angle P \\
225 = 1600 + 1156 - {\rm{2720}} \cdot \cos \angle P \\
225 = {\rm{2756 - 2720}} \cdot \cos \angle P \\
2720 \cdot \cos \angle P = {\rm{2531}} \\
\cos \angle P = \frac{{{\rm{2531}}}}{{2720}} \\
\angle P \approx 21^\circ \\
\end{array}
$
|