Omar Khayyám's geometric solution of a cubic equation
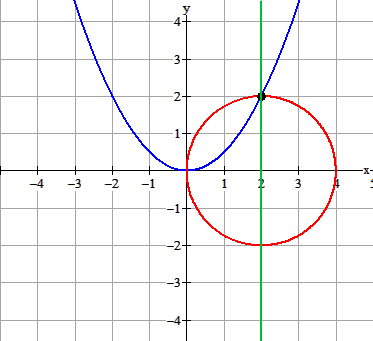
"Omar Khayyám's geometric solution of a cubic equation, for the case $m = 2$, $n = 16$, giving the root $2$. The intersection of the vertical line on the $x$-axis at the center of the circle is happenstance of the example illustrated."
Voorbeeld
De vergelijking $x^3+4x=16$. Volgens Derive is de oplossing gelijk aan $x=2$. We zien $a=2$ en $b=16$.
Volgens Khayyam:
- Teken de parabool $y=\frac{1}{2}x^2$
- Teken de cirkel met een diameter van 4. Dat is $(x-2)^2+y^2=4$.
- Trek een verticale lijn door het snijpunt van de parabool en de cirkel.
- Lees de oplossing af.

$ \begin{array}{l} \left\{ \begin{array}{l} y = \frac{1}{2}x^2 \\ \left( {x - 2} \right)^2 + y^2 = 4 \\ \end{array} \right. \\ \left( {x - 2} \right)^2 + \left( {\frac{1}{2}x^2 } \right)^2 = 4 \\ x^2 - 4x + 4 + \frac{1}{4}x^4 = 4 \\ \frac{1}{4}x^4 + x^2 - 4x = 0 \\ x^4 + 4x^2 - 16x = 0 \\ x(x^3 + 4x - 16) = 0 \\ x = 0 \vee x^3 + 4x - 16 = 0 \\ x = 0 \vee x^3 + 4x = 16 \\ \end{array} $
Benader de oplossing van $x^3+16x=64$ m.b.v. de methode van Khayyam.